New feature release! Live webinar 2/19 @ 11am PST Register now
Table of contents
Table of contents
Key takeaways:
- Capital investment analysis involves evaluating long-term investments to determine their financial and strategic viability.
- Key financial metrics include net present value, internal rate of return, and payback periods.
- Businesses can address common challenges of capital investment analysis through industry benchmarks, sensitivity testing, and contingency planning.
- Modern financial management tools and software streamline and improve the accuracy of capital investment analysis.
Capital investments are a key to a long-term financial strategy and can position your business for sustained growth for years. Making the right decisions about when, where, and how much to invest can help you prevent major setbacks that could take time to overcome.
However, 41% of businesses say the availability of financing has gotten more difficult or more expensive. As capital becomes harder and pricier to obtain, it is increasingly important for businesses to make wise investment decisions. Strong capital investment analysis helps business executives make informed, impactful decisions that can save the company time and money.
Learn how to evaluate capital investments and the challenges businesses face when analyzing them. This information, in combination with enterprise accounting software, can help leadership make informed decisions about capital investment opportunities.
What is capital investment analysis?
Capital investment analysis is a budgeting process that helps a company accurately evaluate the profitability of long-term ventures. Capital investments differ from financial investments in that capital investments focus on core business objectives. Financial investments focus on financial instruments, such as stocks and bonds.
Investment capital can cover a broad range of assets a business may need to fuel future growth, including:
- Real estate
- Equipment
- Machinery
- Reach and development
- Employee training
- Facility construction
- Vehicles
- Strategic acquisitions
The goal of capital investment analysis is to identify the investments that are most likely to yield the highest return on invested capital.
5 key metrics to evaluate capital investments
A capital investment analysis is ultimately a cost-benefit analysis that companies use. The analysis helps businesses determine whether the benefits of a long-term investment are high enough to justify the costs as part of the capital budget. When conducting this analysis, a business may use these five methods to evaluate capital investment opportunities.

1. Net present value (NPV)
Net present value (NPV) measures how much future expected revenue (cash flows) is worth today’s dollars. You'll estimate future cash flows via demand planning and then discount these estimated cash flows to present value. The initial investment cost is subtracted from the discounted present value, resulting in the project's NPV.
A positive NPV means the project is financially worthwhile, while a negative NPV suggests that the financials cannot justify the investment.
2. Internal rate of return (IRR)
The internal rate of return (IRR) is the discount rate at which the NPV equals zero. This rate, or the hurdle rate, is the amount a project must earn to be profitable.
A capital investment with an expected rate of return higher than the IRR would produce a positive NPV and be profitable for the business. Projects with rates of return below the IRR are not profitable.
3. Payback period
The payback period is the expected time to recoup the initial investment. It is a quick, simple assessment of an investment's liquidity, with longer payback periods correlating with more illiquid ventures.
4. Discounted cash flow (DCF)
Discounted cash flow (DCF) stipulates that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow due to its earnings potential. DCF accounts for this by discounting future cash flows back to present value via a discount rate.
DCF is a core component of the NPV calculation discussed earlier. DCF provides the present value of expected future cash flows. The NPV of a capital investment is the DCF less the initial investment costs.
5. Other important considerations for investment analysis
In addition to the financial considerations previously mentioned, there are additional factors that should enter into a capital investment analysis:
- Sensitivity analysis: A sensitivity analysis evaluates how a change in one factor can change the expected profitability of a project. For example, a sensitivity analysis may shift the discount rate up or down a percentage point to gauge how that would impact the NPV of the project.
- Real options: NPV decisions assume a fixed decision. Flexibility is a key element of the business decision-making process. Real options add value by recognizing that businesses are not obligated to take a certain action but can defer, switch, or abandon a project altogether.
- Decision trees: These trees map out all possibilities, decisions, and outcomes in a branching path structure. Decision trees help businesses measure the expected value of each step and better incorporate probabilities and risk into their analysis.
- Environmentally sustainable investment analysis: Making a profit is a business's fundamental purpose, but it isn’t the only issue that companies must consider. The final capital investment analysis should incorporate any social and financial costs related to environmental impact.
For an effective capital investment analysis, you should consider qualitative factors, like the project's strategic fit and how it furthers your competitive advantage.
Why capital investment analysis matters for your business

Capital investment analysis provides powerful benefits for businesses, no matter the size or industry in which they operate. These benefits include:
Informed decision-making
The size and scope of major capital investments make these decisions more challenging and more important to get correct. Without proper analysis, a company may make these choices based on gut feelings or internal company politics.
Instead, businesses must move their capital investment analysis beyond intuition. Leveraging objective financial metrics, including NPV, IRR, and DCF, companies can ensure they’re making smart, profitable investment decisions.
Objective financial metrics clearly illustrate whether a venture is profitable, making it easier for companies to justify investing in projects that carry a large upfront cost.
Optimizing resource allocation
A common bottleneck for corporate growth is raising and accessing capital, which can limit your company’s growth opportunities. Capital investment analysis can help your business allocate capital toward high-impact projects and away from lower, less-profitable opportunities, which is a key to sustained profit growth.
Strategic planning
Profitable projects are about more than just making the financial work, although this is a critical component. Capital investment decisions should also align with your strategic financial planning process to help you make decisions that fit into and reinforce your long-term growth plans.
Maximizing shareholder value
Companies that excel at capital investment analysis invest in projects that are consistently profitable. Thus, they can feel more confident that their capital investments will provide the highest returns to owners.
Not only does effective capital investment analysis improve shareholder value, but it also improves shareholder confidence in the firm. If your company makes decisions based on trusted financial metrics, you can easily communicate to investors and shareholders that you're carefully evaluating the risks and rewards of every opportunity.
Common challenges in capital investment analysis and how to overcome them
Capital investment analysis can prove to be difficult, but with proper planning, you can overcome these challenges:
Projecting accurate future cash flows
The foundation of any capital investment analysis is the expected future cash flows that the project will produce. Estimating these future cash flows is part of that process.
While no company can guarantee how much revenue an investment will produce, thorough research and preparation can lead to more accurate estimates and higher-quality analyses.
Determining the appropriate discount rate
Getting the discount rate right is an important and nuanced step in the capital investment analysis process. An appropriate discount rate directly impacts how a firm values future cash flows.
Sensitivity analysis, industry benchmarks, and market data can all help you verify whether you’re using a fair discount rate in your analysis.
Accounting for unexpected events
No matter how well you plan, the unexpected will occur. Contingency planning and regular re-evaluation will help your growing organization remain agile and productive in evolving circumstances.
When you schedule a demo, you agree to permit Intuit to use the information provided to contact you about Intuit Enterprise Suite and other related Intuit products and services. Your information will be processed as described in our Global Privacy Statement.
Tools to simplify the analysis process
The value of a capital investment analysis hinges on its accuracy. Today, businesses can use a wealth of tools to streamline the capital investment analysis and feel more confident about the accuracy of their analysis.
These resources include the following:
Dedicated calculators for core metrics
Capital investment analysis involves a lot of complex math. Fortunately, user-friendly calculators on the market can handle the heavy lifting when calculating NPV, IRR, and payback periods. You can find these tools online, within spreadsheet software, or integrated with financial planning tools, like Intuit Enterprise Suite.
Resources for advanced analysis
Deeper analytical tools provide valuable insights for complex or higher-risk investments. Sensitivity analysis tools help evaluate how changes in key assumptions, such as sales volume, impact profitability metrics like NPV and IRR. Monte Carlo simulations can model various scenarios and outline their probabilities of success.
You can integrate these tools with dimensional forecasting software to resolve more complicated analyses and build robust future profitability projections.
Frameworks for structured approaches
Established guides and frameworks offer structured methodologies for approaching capital investment analysis. Examples include:
- Reputable financial guides: These guides provide step-by-step processes and best practices from identification to decision.
- Holistic evaluation: Frameworks often consider nonfinancial factors, such as environmental impact or the project's strategic alignment.
- Internal procedures: Well-established internal processes are useful for setting up consistent evaluation processes within your business.
Leveraging Intuit Enterprise Suite for seamless financial data management
Comprehensive business intelligence is the bedrock of any accurate investment analysis. Intuit Enterprise Suite can bring your financial data management to the next level by making it easier to:
- Track costs and revenues: Track all project-related expenditures and expected income streams directly within the Intuit Enterprise Suite.
- Monitor cash flow: Understand the timing of cash inflows and outflows using its reporting features.
- Categorize expenses: Use custom categories or tags to isolate and analyze costs related to specific capital projects.
Boost productivity and enhance profitability
Capital investment is more than just the numbers. It’s about deciding to further your company’s long-term strategic goals. Combining financial data with real-world insights, you can confidently evaluate opportunities, make intelligent business decisions, and improve business efficiency.
The Intuit Enterprise Suite (IES) integrated accounting software offers industry-specific solutions that can enhance profitability, boost productivity, and help your company scale confidently. Learn more about how IES can help simplify your complex business operations.
Running a business means facing risks every day. Some are small. Others can have big financial consequences and shake your company’s future—and lower your enterprise value. A 2025 QuickBooks survey found that 45% of small business owners lost over $10,000 in profits due to low financial literacy, underscoring the need for better financial planning.
That’s where enterprise risk assessment (ERA) can help.
ERA helps you find, understand, and manage risks early, before they turn into problems. It’s a smart approach for better financial management and long-term success. Learn more about ERA, how it works, why it matters, and how you can use it to grow your business.
What is enterprise risk assessment?
Enterprise risk assessment (ERA) is a top-down, firm-wide business strategy to identify and manage potential risks before they disrupt operations. It looks at all areas of your business, and helps you make smarter, safer decisions.
ERA spots everything that could harm your company’s goals, reputation, or financial health, including:
- Market changes
- System failures
- Legal issues
- Natural disasters
- Cybersecurity breaches
- Supply chain disruptions
- Reputational damage
ERA is the first step of the broader process called enterprise risk management (ERM), which focuses on planning and responding to the risks you identify using ERA. Though often used interchangeably, ERA is technically just one phase of ERM.
How ERA brings teams and leaders together
Enterprise risk assessment takes a wide-angle view of your business. It brings together leaders across departments and calls for decisions at the top level. The idea is to make risk a shared responsibility, not something left to just one team.
Key elements of this approach include:
- Firm-wide visibility: Every area of the business is reviewed, from finance to operations to IT.
- Senior involvement: C-level leaders, including the CFO, play a central role in risk decisions.
- Transparency: Risks and responses are clearly communicated across teams and departments.
- Industry-wide use: ERM is common in high-stakes fields like aviation, construction, public health, finance, and insurance.
- Dedicated teams: Many companies build ERM teams, often led by a CRO to guide the strategy and keep it aligned with business goals.
5 Key components of enterprise risk management
ERM has five core components that work together to help you manage risk thoughtfully and consistently. These pieces make sure risks are understood, discussed, and acted on at every level of the company.

1. Governance and culture
Good governance sets the tone for how seriously your company takes risk. It ensures strong oversight and clear responsibilities from the top down. Culture shapes how people think about and handle risk each day.
Key focus areas include:
- Risk oversight by the board
- Clear roles and operating structures
- A culture that supports ethical behavior
- Shared core values
- Hiring and developing the right people
Together, governance and culture build a strong base for your risk efforts.
2. Strategy and objective setting
ERM helps you match your risk appetite with your long-term strategy. It ensures your team understands how much risk is acceptable and aligns goals to fit.
This step includes:
- Defining your risk appetite
- Setting clear, measurable business objectives
- Evaluating different strategies and paths
- Choosing goals that support your mission
By linking strategy and risk early on, you avoid surprises down the road.
3. Performance
ERM looks at how risks could impact your business goals and how to handle them. It helps you focus on the most serious risks and take action quickly.
Key tasks here include:
- Identifying and assessing risks
- Comparing risks against your risk appetite
- Choosing the right response—accept, avoid, reduce, or share
- Viewing all risks together as a full portfolio
- Reporting results to leadership and stakeholders
This step keeps risk tied to real performance.
4. Review and revision
Over time, your business changes, and your ERM process should change with it. This step helps you check if your plan is still working and adjust as needed.
You’ll want to:
- Review how well your ERM system performs
- Spot major internal or external changes
- Identify areas to improve
- Make updates to stay effective
It’s about keeping your risk strategy fresh and relevant to boost business efficiency.
5. Information, communication, and reporting
To manage risk well, people need the right information at the right time. ERM ensures you gather, share, and use data to protect your business.
This includes:
- Pulling insights from internal and external sources
- Using IT systems to track risk-related data
- Sharing updates across departments
- Communicating clearly to get team buy-in
When everyone understands the risks, they can take the right steps to manage them.
How to implement enterprise risk management practices
Enterprise risk management practices look different for every company. Your approach depends on your company size, industry, goals, and how much risk you're willing to take on. Still, a few best practices can help guide any business toward a stronger, more thoughtful ERM plan.
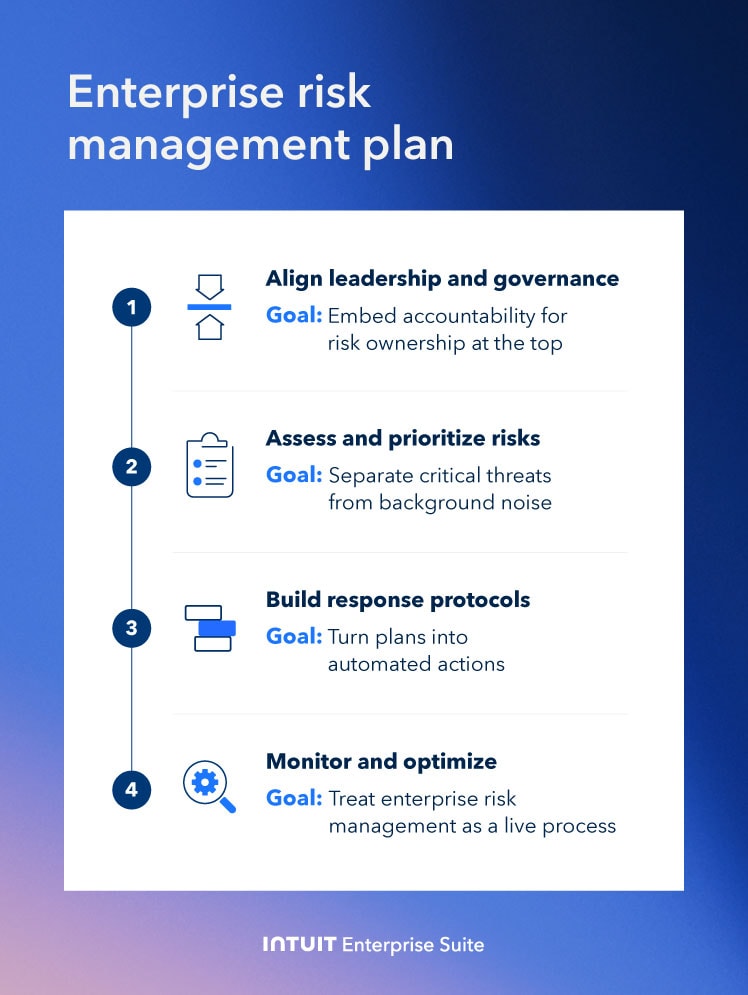
1. Define your company's risk philosophy
Begin by understanding how your company views risk—whether it’s risk-averse, risk-neutral, or risk-tolerant. Engage in strategic conversations with executives, department heads, and other key stakeholders to clarify your risk tolerance. Assessing your full risk profile will help define which risks are acceptable and which you need to avoid or mitigate.
2. Create action plans
Once you’ve identified your risks, outline clear steps to mitigate them. Define specific steps to protect your assets and safeguard your company’s future. For example, if a cybersecurity breach is a risk, your action plan might include isolating affected systems, notifying customers, and restoring data from backups.
3. Be creative
Risk isn’t always predictable. While you can’t plan for every outlandish scenario, you should engage in scenario planning. It involves thinking through possible disruptions, such as supply chain issues, regulatory changes, or economic downturns, and determining how your business will respond.
4. Communicate priorities
Make sure everyone knows which risks matter most. Share top risks across teams and clarify which ones to avoid. Also, explain what to do if a key risk does occur.
Ensure that everyone—from leadership to team members—understands which risks matter most and knows how to respond. Write your priorities down and communicate them often to keep everyone aligned and ready to take quick, consistent action when risks arise.
5. Assign responsibilities
Assign parts of your risk plan to specific roles, not just people. That way, even if someone leaves, their responsibilities stay clear. This helps keep your plan running smoothly at all times.
6. Maintain flexibility
Your ERM strategy should evolve with your company. As you grow or change direction, your risks will change too. Stay flexible so you can adjust without starting from scratch.
7. Leverage technology
Use ERM software, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, or digital dashboards to organize everything in one place. These tools help you track risks, run reports, and monitor internal controls in real time.
8. Continually monitor
Don’t set it and forget it. Check in regularly to see if people are following the plan. Track how well your risk responses are working and where improvements are needed.
9. Use metrics
Set clear, measurable targets using simple tools like SMART goals. These help you know if you’re on track and hold teams accountable for results. You can also set KPIs for your business and measure them regularly.
6 Types of risk that enterprise risk assessment (ERA) addresses
ERA can help your company prepare for almost any type of risk that could threaten its survival or slow its growth. These risks come in many forms—some are external, some internal—but all can affect your enterprise value. Below are the main types of risks ERM can handle.

Compliance risk
Compliance risk arises when your business fails to meet rules, laws, or standards. This could mean not following tax codes, industry regulations, or financial reporting requirements like GAAP. It can lead to fines, delays, or a damaged reputation. ERM helps make sure teams know the rules and follow them on time, every time.
Legal risk
Legal risk shows up when your business faces lawsuits, contract disputes, or penalties tied to legal obligations. For example, a disagreement over billing terms with a vendor or partner could result in costly litigation. With ERM, you can reduce this risk by keeping contracts clear, updated, and well-managed.
Compliance is about following external rules; legal risk includes lawsuits, contracts, and disputes. Tracking them separately to create targeted responses that reduce penalties and protect your company’s reputation.
Strategic risk
Strategic risk threatens your big-picture goals. Think about new competitors, changing customer habits, or market shifts that make your strategy obsolete. For instance, if you’re the lowest-cost provider but someone else offers a cheaper solution, your entire business model is at risk.
Use strategic financial planning to ensure your financial strategy aligns with your broader goals, and integrate ERM to identify these risks early.
Operational risk
Operational risk impacts your day-to-day functions. It includes everything from power outages to supplier delays to natural disasters. If your warehouse floods or your delivery system fails, you could lose time, money, or customer trust. ERM plans help you prepare for—and bounce back from—these disruptions. A warehouse management system can help, too.
Security risk
Security risk involves any threat to your physical or digital assets. This could be someone stealing client data, breaking into your office, or misusing company systems. Weak security can damage trust and bring legal trouble. Having efficient enterprise business intelligence (BI) and ERM helps tighten controls and keep your information and property safe.
Financial risk
Financial risk affects your company’s money and stability. It includes issues like interest rate changes, credit problems, and currency fluctuations. For example, if you operate globally and the dollar drops in value, you could take a hit. ERM keeps your financial risks visible and manageable.
You can also use tools like Intuit Enterprise Suite (IES) to manage financial risks and improve decision-making. IES offers real-time financial reporting, AI-driven forecasting, and automated workflows to help you identify risks early and adjust your strategy quickly.
When you schedule a demo, you agree to permit Intuit to use the information provided to contact you about Intuit Enterprise Suite and other related Intuit products and services. Your information will be processed as described in our Global Privacy Statement.
Business tools your company can use for enterprise risk assessment success
To get the most from enterprise risk assessment, you need more than spreadsheets or one-off reports. You need the right business tools that can connect the dots and turn insights into action. When choosing a tool, look for the following features to manage your enterprise performance smoothly.
Unified data management and reporting capabilities
A successful risk assessment starts with clean, organized data. If your financials, sales, or operations data live in different systems—or worse, aren’t accessible at all—it’s nearly impossible to get accurate results.
Integrated platforms like Intuit Enterprise Suite give you one place to manage your data, track inputs, and generate real-time reports. With a clear view of everything in one dashboard, you can build your ERM strategy on solid ground.
AI-powered forecasting and financial planning
Predictive analytics can show you what might happen next, but that’s only useful if it feeds into your planning process. Your team needs to take risk scores, projected losses, or trend data and plug them into your overall strategy.
Modern platforms like IES do just that. With built-in business forecasting and advanced business intelligence capabilities, they combine risk insights with financial planning tools. This helps you prepare for what’s ahead and build smarter, more flexible budgets.
Take your time to pick a tool. The right tool turns a red flag into a real-time adjustment, whether it’s a financial trigger, a staffing shift, or a workflow change, keeping your business agile and ahead of risk.
Features for automating financial workflows and payments
Knowing which transactions carry higher risk is valuable. Acting on that information automatically is even better. Predictive insights can help trigger payment holds, approvals, or added checks for flagged activity.
You can use tools like Intuit Assist that offer automation features that tie risk directly to your financial processes. Whether it’s flagging unusual payments or speeding up low-risk approvals, automated accounting saves time and reduces exposure.
Integrated workforce management features
ERM also applies to people, not just processes. Predictive tools can help forecast staffing needs, spot patterns in employee turnover, or flag productivity dips. But your team needs tools to respond in real time.
With integrated workforce features, platforms like QuickBooks allow you to take action—adjust schedules, shift resources, or prepare for hiring needs—based on those predictive models. This makes human capital management easier and keeps your workforce aligned with your business risk strategy.
Use Intuit Enterprise Suite to simplify strategic enterprise risk assessment
Enterprise risk assessment isn’t just about avoiding problems—it’s about building a stronger, smarter business. When you understand your risks, you make better decisions, protect your assets, and plan with more confidence. It supports everything from daily operations to long-term strategy, helping you stay focused on growing your business.
Intuit Enterprise Suite offers a lot of features that give you the structure and insights you need to make ERM practical. From unified data to automated workflows and AI-powered forecasting, it helps you manage risks while keeping your business moving forward.
Explore more about our enterprise financial management solution today and build a more resilient future for your business.
Customer stories

How FEFA Financial is growing with Intuit Enterprise Suite—without migrating to an ERP

How this mission-driven, employee-owned company created efficiencies with Intuit Enterprise Suite

Why this camping business chose Intuit Enterprise Suite over NetSuite

Migrating to Intuit Enterprise Suite took 2 hours (with zero disruption) for this aspiring $50M revenue business










